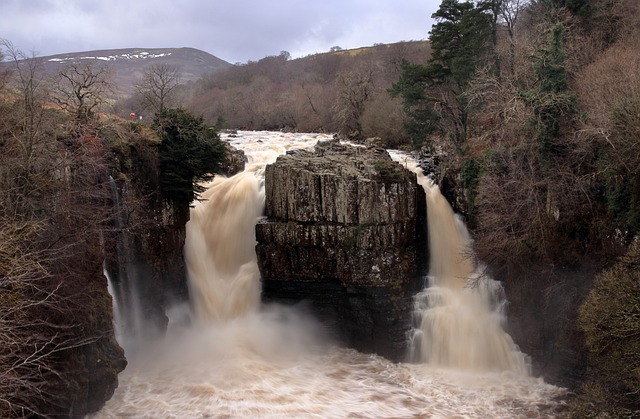
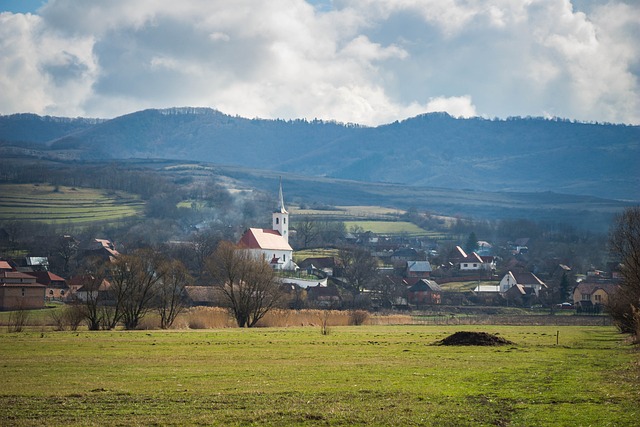
The southeastern US boasts a rich agricultural history, with farmland and ranching shaping the region's past and present. Centuries-old practices, passed down through generations, coexist with modern real estate developments, highlighting a harmonious balance between tradition and progress. Native American cultures like the Cherokee and Chickasaw pioneered farming, later joined by European settlers who expanded operations, making the area renowned for its productive farmland. Today, this historical heritage drives the region's vibrant real estate market, attracting those seeking unique charm and investment potential in historic farmland. Sustainable techniques continue to ensure the land supports both residential growth and thriving agricultural communities.
“The Southeastern United States, with its rich farmland and expansive ranching terrain, boasts a unique blend of historical significance and modern opportunities. This region, steeped in agricultural tradition, has witnessed a transformation over centuries, from Native American cultivation to European settlements, shaping today’s diverse landscapes. From the rolling hillsides and lush forests to the vital water bodies and fertile soils, each topographical feature contributes to the area’s enduring appeal as prime real estate for both traditional ranching and emerging agro-tourism ventures.”
The Rich History and Cultural Significance of Southeastern Farmland

The southeastern United States boasts a rich agricultural heritage, where farmland and ranching territories have played a pivotal role in shaping the region’s history and culture. This diverse landscape, characterized by fertile soils and mild climates, has been nurtured by generations of farmers and ranchers who have contributed to the area’s vibrant real estate market. The region’s agrarian roots run deep, dating back to colonial times when European settlers cleared land for farming and established thriving plantations.
Over the centuries, these agricultural practices evolved, adapting to changing economic landscapes and cultural influences. The southeastern farmland became a vital part of the country’s food production, supplying both local communities and expanding urban centers. Today, the region continues to be recognized for its high-quality agricultural output, attracting investors and enthusiasts alike who appreciate the unique charm and potential of this historic real estate.
– Exploring the roots of agricultural practices

The agricultural landscape of Southeastern farmland and ranching territory is deeply rooted in history, reflecting centuries of human settlement and adaptation to the region’s unique geography and climate. Early settlers found fertile soils and abundant water sources, ideal for cultivating crops and raising livestock. Over time, these areas evolved into thriving agricultural hubs, with practices passed down through generations, shaping the region’s identity.
Exploring the roots of agricultural practices in this region reveals a rich tapestry of methods that have endured and adapted. Traditional farming techniques, such as crop rotation and sustainable livestock management, have been refined and integrated with modern real estate developments, ensuring the land continues to support both residential growth and vibrant agricultural communities. This harmonious coexistence showcases a delicate balance between historical traditions and contemporary progress in Southeastern farmland.
– Native American influences and early European settlements

The history of southeastern farmland and ranching territory is deeply intertwined with Native American cultures and early European settlements. For centuries, indigenous tribes like the Cherokee and Chickasaw called this region home, cultivating lush farms and establishing trading routes that crisscrossed the landscape. Their profound connection to the land shaped the area’s agricultural traditions and ecological stewardship.
European settlers began arriving in the 16th and 17th centuries, drawn by the fertile soil and abundant resources. These early pioneers built upon the existing agricultural practices and gradually expanded farming and ranching operations. Over time, the region became known for its productive farmland, attracting real estate investors and farmers seeking vast, unencumbered land for crop cultivation and livestock grazing.