Manufacturing facilities require specialized real estate with ample space for machinery, efficient workflow design, specific environmental controls, vast storage areas, robust safety features, and accessible layouts. Strategic location selection is key, considering proximity to raw materials, transportation networks, labor markets, and local infrastructure like utilities. These factors optimize functionality, productivity, and long-term viability in modern manufacturing operations.
Manufacturing facilities play a pivotal role in today’s economy, demanding specialized features tailored to their unique operational needs. From expansive floor plans to strategic loading docks and advanced infrastructure, optimizing industrial real estate is crucial for efficient production. This article explores the key considerations—including location—that define successful manufacturing facility design, ensuring operations run smoothly and competitively in the modern marketplace. Dive into these essential aspects of real estate planning for maximum productivity.
Understanding the Unique Needs of Manufacturing Facilities

Manufacturing facilities, unlike traditional offices or retail spaces, have distinct and specialized requirements due to the nature of their operations. When considering real estate for such facilities, it’s crucial to grasp these unique needs to ensure optimal functionality and productivity. These include ample space for machinery, efficient layout design to facilitate smooth workflow, and specific environmental controls like temperature regulation and ventilation to cater to industrial processes.
The real estate landscape for manufacturing must also accommodate the storage of raw materials and finished goods, often requiring vast warehouse-like areas. Additionally, safety is paramount; features such as fire suppression systems, emergency exits, and robust structural integrity are essential. The layout should be designed with accessibility in mind, considering the movement of heavy equipment and materials to streamline production processes.
Key Specialized Features in Industrial Real Estate
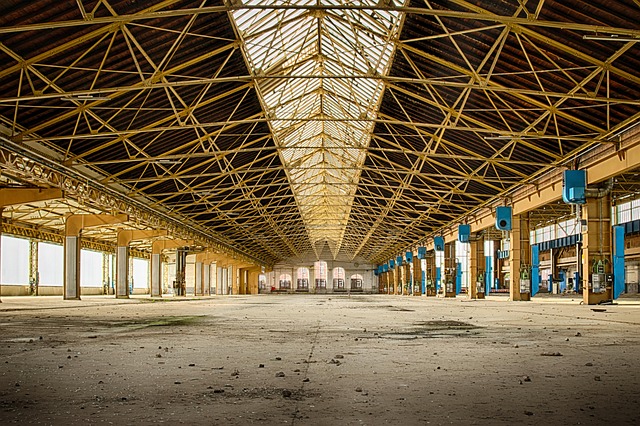

Manufacturing facilities need real estate with key specialized features tailored for industrial operations. These include ample floor space to accommodate large machinery and flexible layouts that can be reconfigured to support changing production needs. High ceilings are often essential for efficient material handling and storage, while robust infrastructure like strong foundations and reliable power supply are crucial for heavy manufacturing processes.
Proximity to transportation networks, both road and rail, facilitates the movement of raw materials and finished goods. Access to water sources can be beneficial for certain industries involving liquid handling or cooling systems. Additionally, modern industrial real estate often incorporates eco-friendly features such as energy-efficient design, natural lighting, and sustainable waste management systems, reflecting a growing emphasis on environmental responsibility in manufacturing.
The Impact of Strategic Location on Manufacturing Facility Design

The strategic location of a manufacturing facility plays a pivotal role in its design and overall operational efficiency. When selecting a site, manufacturers must consider factors such as proximity to raw material sources, transportation networks, and labor markets. For instance, choosing a region with abundant natural resources nearby can streamline logistics and reduce costs associated with materials supply. Similarly, facilitating efficient transport connections ensures timely delivery of finished goods to distribution centers or end-users.
Real estate considerations extend beyond physical resources; they also encompass the local infrastructure and regulatory environment. Access to reliable utilities like electricity, water, and internet connectivity is essential for modern manufacturing processes. Additionally, understanding local zoning laws and environmental regulations can significantly impact facility layout and construction plans. These strategic location factors collectively shape the design of manufacturing facilities, influencing their productivity, sustainability, and long-term viability.