Regular Maintenance: Key to Boosting Real Estate Property Value
Regular maintenance is crucial for real estate investors, ensuring well-kept properties that are mor…….
In today’s dynamic world, the concept of property maintenance has evolved far beyond mere upkeep. It has become a strategic practice that influences economic growth, urban development, and the overall well-being of communities. This article aims to explore the multifaceted world of property maintenance, shedding light on its significance, global impact, and future potential. From understanding the fundamentals to analyzing emerging trends, we will navigate through various aspects that shape this industry.
Definition and Scope:
Property maintenance refers to the ongoing care, repair, and improvement of real estate properties, including residential buildings, commercial spaces, and infrastructure. It involves a range of activities designed to preserve the value, safety, and functionality of assets over time. This process encompasses both preventive measures to avoid deterioration and corrective actions to address existing issues.
Core Components:
Regular Inspection: Conducting routine inspections is vital. It includes checking for structural integrity, identifying wear and tear, and assessing potential hazards. For instance, a monthly inspection of apartment buildings can help manage pest infestations and ensure timely repair of leaks.
Repairs and Upkeep: This involves addressing issues like broken fixtures, faulty plumbing, electrical repairs, and landscaping maintenance. Prompt action on minor problems prevents them from escalating into costly major repairs.
Preventive Maintenance: A proactive approach that includes cleaning, painting, sealing, and lubricating to prolong the lifespan of various components. For example, regular sealing of concrete surfaces can prevent damage from weather conditions.
Modifications and Renovations: Occasionally, properties may require significant transformations to adapt to changing needs or market demands. This could involve expanding living spaces, modernizing amenities, or converting structures for new uses.
Historical Context:
The practice of property maintenance has deep roots in human history. Ancient civilizations employed techniques to preserve their dwellings, such as using natural materials and simple construction methods. Over time, with the evolution of urban centers, property maintenance evolved into a specialized field. The Industrial Revolution brought about new building materials and construction techniques, increasing the complexity of maintenance tasks. In modern times, with the rise of real estate as a significant economic sector, efficient property maintenance has become a critical aspect of asset management.
Property maintenance is not limited to specific regions; it is a global phenomenon that varies in approach and intensity across different countries. Here’s an overview:
| Region | Unique Aspects & Trends |
|---|---|
| North America | Emphasis on energy-efficient practices, adoption of smart home technology for remote monitoring, and a robust market for property management services. |
| Europe | Strict environmental regulations driving the use of sustainable materials and eco-friendly maintenance practices. The rise of co-living spaces is also a notable trend. |
| Asia Pacific | Rapid urbanization leading to high demand for maintenance services. China, in particular, has seen significant investment in smart cities, integrating property maintenance with urban planning. |
| Middle East & Africa | Focus on luxurious amenities and high-end property development. The region is also witnessing the impact of climate change, prompting adaptations in maintenance strategies. |
These trends reflect how cultural, economic, and environmental factors influence the practice of property maintenance worldwide.
The property maintenance industry plays a pivotal role in the global economy, with various interconnected dynamics:
Market Size: According to a 2021 report by Fortune Business Insights, the global property maintenance market size was valued at USD 493.7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 658.1 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 4.6%.
Investment and Spending: Property owners and investors allocate significant funds for maintenance, with varying budgets based on property type, location, and age. For instance, commercial real estate maintenance can be more extensive due to the complexity of these structures.
Employment Impact: The industry supports a substantial workforce, including skilled tradespeople like plumbers, electricians, and painters, as well as property managers and maintenance supervisors.
Economic Indicators: Property maintenance spending is closely tied to overall economic health. During economic downturns, maintenance may be prioritized less, while booms can drive increased investment in improving properties.
Technology has revolutionized the way property maintenance is conducted, enhancing efficiency and opening new possibilities:
Smart Home Systems: Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable remote monitoring of properties, allowing for immediate response to issues like leaks or power outages. Smart thermostats optimize energy use, reducing maintenance costs.
Drone Technology: Drones are being used for detailed building inspections, especially in hard-to-reach areas or on large-scale properties. They provide aerial imagery and data, aiding in faster and more accurate assessments.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR can guide maintenance staff through complex repair procedures, while VR simulations help train workers and plan renovations virtually.
Data Analytics: Advanced analytics predict maintenance needs by analyzing historical data, building performance, and environmental factors. This enables proactive maintenance planning.
The property maintenance market can be segmented based on various criteria:
Property Type: Residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional facilities each have distinct maintenance requirements.
Services Offered: Inspection, repair, upkeep, renovation, and property management are common service categories. Specialized services include disaster recovery, landscaping, and security systems maintenance.
Client Base: Segments include individual homeowners, real estate investment trusts (REITs), property management companies, and government agencies responsible for public infrastructure.
Regulatory bodies worldwide enforce standards to ensure safe and sustainable property maintenance practices:
Building Codes: Local governments mandate specific construction and maintenance practices to ensure structural integrity and safety. These codes cover aspects like fire safety, plumbing, and electrical work.
Environmental Regulations: Many regions have laws governing the use of environmentally friendly materials, waste management during renovations, and energy efficiency standards.
Health and Safety Standards: Maintaining safe working conditions for maintenance staff is crucial. This includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and training on hazard identification and mitigation.
The industry is poised for further transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands:
Sustainability Focus: The push for eco-friendly practices will intensify, with an emphasis on using sustainable materials, energy-efficient systems, and green maintenance techniques.
Digital Twin Technology: Creating digital replicas of physical properties allows for detailed monitoring, predictive analytics, and remote management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI can optimize maintenance schedules, predict equipment failures, and enhance decision-making processes by analyzing vast datasets.
Remote Work Opportunities: The rise of remote work may lead to more distributed maintenance teams, utilizing technology for efficient communication and collaboration.
Property maintenance is an ever-evolving industry that plays a critical role in shaping urban landscapes and supporting economic growth. By embracing technological advancements, prioritizing sustainability, and adapting to global trends, the industry can enhance its efficiency and contribute to smarter, more resilient communities. As we look ahead, the future of property maintenance promises innovative solutions that will continue to shape the built environment for generations to come.
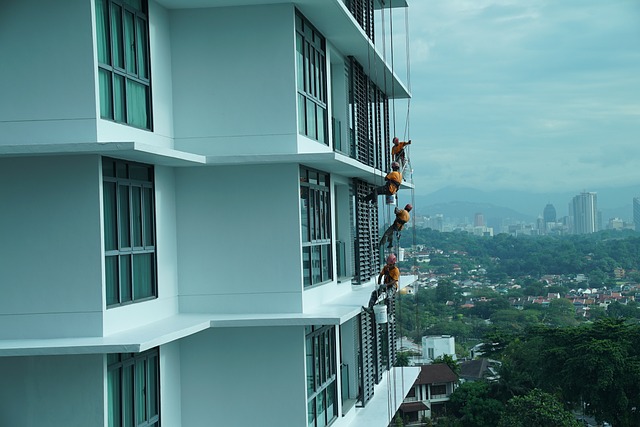

Regular maintenance is crucial for real estate investors, ensuring well-kept properties that are mor…….

Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving and enhancing property value in the dynamic real estat…….

Regular appliance maintenance and inspections are essential strategies for real estate investors to…….

In a competitive real estate market, first impressions are key. Regular upkeep, from fixing minor re…….

Regular maintenance is crucial for preserving and increasing the value of real estate assets, preven…….
In the competitive real estate market, proactive care is a game-changer. This strategic approach aim…….

Regular maintenance is paramount in real estate to preserve and increase property value. Well-mainta…….

In volatile real estate markets, preparing for unforeseen emergencies is crucial for investors and h…….