Modified gross splits in real estate offer a flexible revenue distribution model where agents earn from a percentage of the gross sales price, fostering transparency and partnerships. This shift from traditional practices promotes collaboration among landlords, tenants, and service providers for efficient operations. The model benefits clients with personalized services, open communication, and aligned financial interests, potentially revolutionizing real estate interactions.
In today’s evolving real estate landscape, understanding modified gross splits is crucial for both agents and clients. This innovative model redefines traditional commission structures by shifting responsibilities and revenue sharing dynamics. By delving into this new paradigm, we explore key responsibilities now borne by different parties, the implications for industry players, and how it shapes the future of transactions in real estate.
Understanding Modified Gross Splits in Real Estate
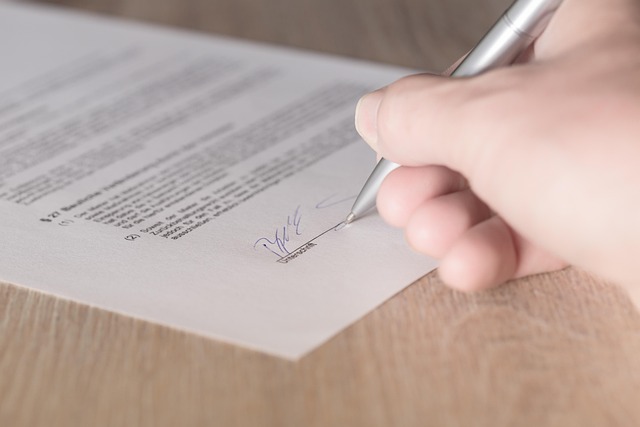

In the dynamic world of real estate, understanding modified gross splits is crucial for both investors and agents. Modified gross splits refer to a unique arrangement where a property’s revenue is distributed among multiple parties, often including a listing agent, selling agent, and a brokerage firm. This structure differs from traditional commission-based models, offering a more intricate approach to compensation. By allocating a percentage of the gross sales price rather than relying solely on commissions, modified gross splits provide flexibility and can incentivize agents to drive higher sales volumes.
This concept is particularly relevant in today’s competitive real estate landscape where efficient revenue sharing is essential. In essence, it allows for a more transparent and potentially lucrative partnership between all involved parties. For investors, understanding this model enables informed decision-making when choosing listing agents or negotiating contracts, ensuring a fair distribution of proceeds from property sales.
Key Responsibilities Shifting in this Model

In a modified gross splits model, the key responsibilities within the real estate industry undergo a significant transformation. Traditionally, agents focused primarily on sales and leasing activities, but this new approach introduces a more collaborative framework. Here, the emphasis shifts to managing relationships between landlords, tenants, and service providers, ensuring seamless operations.
Instead of handling every aspect in-house, real estate professionals now coordinate efforts across various specialized teams. This includes tasks like property maintenance, tenant screening, rent collection, and legal compliance. Such a shift not only improves efficiency but also allows for better resource allocation, providing clients with more tailored and responsive services within the dynamic real estate market.
Implications for Agents and Clients Alike

In the realm of real estate, modified gross splits represent a significant shift in traditional agency structures, with profound implications for both agents and clients. For agents, this new model can offer enhanced flexibility, allowing them to tailor their services more precisely to individual client needs. Instead of a rigid commission structure, modified gross splits provide an opportunity for agents to earn based on performance and the value they bring to the table. This change empowers agents to focus on building long-term relationships with clients, fostering trust, and offering specialized knowledge.
Clients, too, stand to gain from this evolution. By participating in a modified gross split arrangement, clients can better align their financial interests with their agent’s goals, leading to more personalized service. It encourages open communication and collaboration, ensuring that both parties are invested in achieving the best possible outcomes. In real estate, where relationships matter, this innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize how agents and clients interact, creating a more dynamic and mutually beneficial environment.